
This is eLearning module was designed to give teachers the basic understanding of generative AI and its benefits in education. The module was created for a designed-based research project completed as part of a graduate program at Western Governors University. The eLearning is designed around the use of choice boards and giving the learner the freedom of how they want to learn the content..
Audience: Teachers that want to shorten their lesson preparation time.
Responsibilities: Research, needs analysis, instructional design (action mapping, storyboarding, mockups, prototype, full build), visual design, eLearning development
Tools Used: Canvas LMS, Synthesia, Google Docs, Google Slides, Canva, Chat GPT, Brisk Teaching
Case Study: Scenario-Based eLearning for Food Storage Training
Overview
This eLearning module was designed as part of a research project for the graduate program at Western Governors University. The goal was to give teachers an understanding of generative AI and demonstrate how it can help reduce lesson preparation time. The module incorporates choice boards, giving teachers the freedom to choose how they want to learn the content based on their preferences.
The Problem
Teachers at Jefferson Elementary were struggling with lesson preparation time. Most teachers were unaware of the potential benefits of generative AI in the classroom. They lacked knowledge about AI applications in education, resulting in a skills gap.
Key Issues:
- Teachers were unaware of the time-saving benefits of generative AI.
- There was a significant gap in understanding how AI could be used to enhance lesson preparation.
- Teachers needed a way to practice and apply generative AI tools in a meaningful way for their classrooms
The Solution
To address the problem, a 30-minute eLearning module was created to teach teachers about generative AI and its applications in education. The solution included:
- Choice Boards: Learners could choose how they wanted to consume the content—videos, articles, or infographics—giving them flexibility in their learning process.
- AI Tool Practice: Teachers applied their newly acquired knowledge by using AI tools, such as ChatGPT, to create lesson materials.
- Practical Application: The eLearning module allowed teachers to practice using generative AI tools, helping them transfer the knowledge to their professional teaching.
Project Process
1. Analysis Phase
- Needs Assessment: Conducted discussions with teachers to understand their pain points around lesson preparation and the potential role of AI.
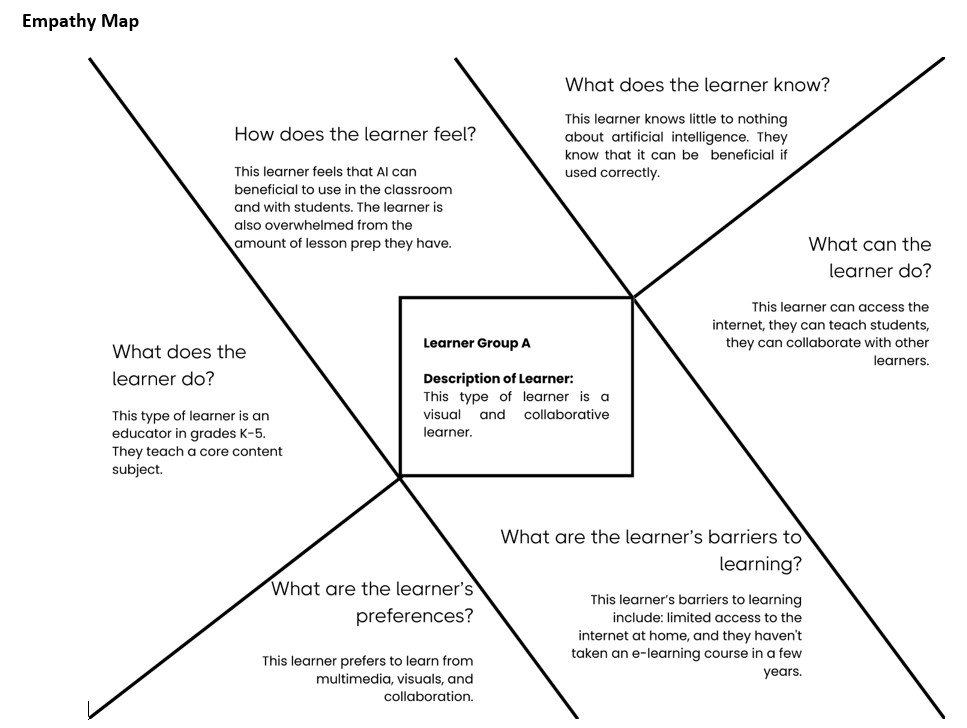
- Empathy Map: Collaborated with the SME to create an empathy map, answering key questions about the learners’ knowledge, feelings, behaviors, preferences, and barriers.
- Learner Personas: Developed personas based on the empathy map to inform the course design and content delivery.

2. Design Phase
- Learning Goal: Learners will be able to explain generative AI and its benefits in education.
- Learning Objectives:
- Explain what generative AI is.
- Identify at least two ways to use generative AI in the classroom.
- Create prompts using chatbots like ChatGPT.
- Create lesson materials using generative AI tools.
- Explain what generative AI is.
3. Development Phase
- Content Creation: Developed content that explained generative AI basics and its uses in the classroom, while integrating choice boards for flexibility in how the material was consumed.
- Interactive Elements: Used choice boards to ensure teachers could select how they wanted to engage with the material.
- Tool Integration: Incorporated generative AI tools for teachers to experiment with and create lesson materials.
4. Implementation Phase
- The project was implemented with teachers from Jefferson Elementary. They were asked to complete the module on their own time and report back. Quantitative and qualitative data were also gathered throughout the module from quizzes and assignments.
5. Evaluation Phase
Quantitative data was taken from a pre=test and post-test that the learners completed during the module. The data is as follows:
- Pre-test: Average score of 49%.
- Post-test: Average score of 72%.
- Growth: An average knowledge increase of 23% among participants.
Qualitative data was taken from a post-survey quiz the learners completed. Coding was used to analyze the data in order to identify key themes.
- Theme 1: Choice boards made learning relevant: Participants could apply their learning directly to their classroom, making the content immediately useful.
- Theme 2: Choice boards empowered self-directed learning: Teachers felt in control of their learning, allowing them to choose what they wanted to learn and how they learned it.
Reflection
- Key Insights:
- Choice boards as a learning tool: Teachers appreciated the flexibility to choose how they engaged with the content, which helped keep them motivated and active in their learning.
- Generative AI in education: The eLearning successfully introduced teachers to AI tools, empowering them to streamline lesson planning and utilize AI in a practical way.
- Data-driven improvement: The pre-test and post-test results showed measurable growth, indicating that the learning objectives were met successfully.
- Choice boards as a learning tool: Teachers appreciated the flexibility to choose how they engaged with the content, which helped keep them motivated and active in their learning.
- Challenges and Successes:
- One challenge was ensuring the AI tools were simple enough for teachers with little experience with technology, but the interactive components and practical application made the learning process more engaging.
- The success of this module lies in the practical integration of AI tools, which allowed teachers to see the immediate benefits of the technology in their daily tasks.
- One challenge was ensuring the AI tools were simple enough for teachers with little experience with technology, but the interactive components and practical application made the learning process more engaging.
- Skills and Tools
- This project enhanced my ability to design eLearning using flexible learning structures (like choice boards) and integrate AI tools into educational content. I also gained more experience with data analysis, especially in analyzing both quantitative and qualitative results to assess the effectiveness of the training.
Conclusion
This eLearning module successfully helped teachers understand and apply generative AI tools in their lesson planning. By giving teachers the flexibility to choose how they learned and allowing them to practice with real AI tools, the course met its goal of shortening lesson preparation time. The combination of choice-based learning and practical application contributed to measurable improvements in teachers’ knowledge and confidence with AI in education.